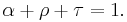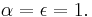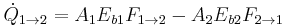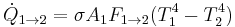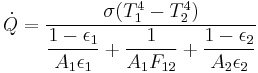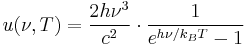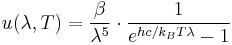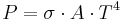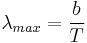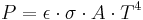Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation.
Examples of thermal radiation include visible light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction--a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.
Sunlight is thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.
If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation.[1] Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.[2]
In engineering, thermal radiation is considered one of the fundamental methods of heat transfer, although a physicist would likely consider energy transfer through thermal radiation a case of one system performing work on another via electromagnetic radiation, and say that heat is a transfer of energy that does no work. The difference is strictly one of nomenclature.
Contents |
Overview
Thermal radiation is the emission of electromagnetic waves from all matter that has a temperature greater than absolute zero.[3] It represents a conversion of thermal energy into electromagnetic energy. Thermal energy is the collective mean kinetic energy of the random movements of atoms and molecules in matter. Atoms and molecules are composed of charged particles, i.e. protons and electrons and their oscillations result in the electrodynamic generation of coupled electric and magnetic fields, resulting in the emission of photons, radiating energy and carrying entropy away from the body through its surface boundary. Electromagnetic radiation, or light, does not require the presence of matter to propagate and travels in the vacuum of space infinitely far if unobstructed.
The characteristics of thermal radiation depends on various properties of the surface it is emanating from, including its temperature, its spectral absorptivity and spectral emissive power, as expressed by Kirchhoff's law.[3] The radiation is not monochromatic, i.e. it does not consist of just a single frequency, but comprises a continuous dispersion of photon energies, its characteristic spectrum. If the radiating body and its surface are in thermodynamic equilibrium and the surface has perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, it is characterized as a black body. A black body is also a perfect emitter. The radiation of such perfect emitters is called black-body radiation. The ratio of any body's emission relative to that of a black body is the body's emissivity, so that a black body has an emissivity of unity.
Absorptivity, reflectivity, and emissivity of all bodies are dependent on the wavelength of the radiation. The temperature determines the wavelength distribution of the electromagnetic radiation. For example, fresh snow, which is highly reflective to visible light (reflectivity about 0.90), appears white due to reflecting sunlight with a peak wavelength of about 0.5 micrometres. Its emissivity, however, at a temperature of about -5 °C, peak wavelength of about 12 micrometres, is 0.99.
The distribution of power that a black body emits with varying frequency is described by Planck's law. At any given temperature, there is a frequency fmax at which the power emitted is a maximum. Wien's displacement law, and the fact that the frequency of light is inversely proportional to its wavelength in vacuum, mean that the peak frequency fmax is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the black body. The photosphere of the Sun, at a temperature of approximately 6000 K, emits radiation principally in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Earth's atmosphere is partly transparent to visible light, and the light reaching the surface is absorbed or reflected. Earth's surface emits the absorbed radiation, approximating the behavior of a black body at 300 K with spectral peak at fmax. At these lower frequencies, the atmosphere is largely opaque and radiation from Earth's surface is absorbed or scattered by the atmosphere. Though some radiation escapes into space, it is absorbed and subsequently re-emitted by atmospheric gases. It is this spectral selectivity of the atmosphere that is responsible for the planetary greenhouse effect, contributing to global warming and climate change in general.
The common household incandescent light bulb has a spectrum overlapping the black body spectra of the sun and the earth. A portion of the photons emitted by a tungsten light bulb filament at 3000 K are in the visible spectrum. However, most of the energy is associated with photons of longer wavelengths; these do not help a person see, but still transfer heat to the environment, as can be deduced empirically by observing a household incandescent light bulb. Whenever EM radiation is emitted and then absorbed, heat is transferred. This principle is used in microwave ovens, laser cutting, and RF hair removal.
Unlike conductive and convective forms of heat transfer, thermal radiation can be concentrated in a tiny spot by using reflecting mirrors. Concentrating solar power takes advantage of this fact. In many such systems, mirrors are employed to concentrate sunlight into a smaller area. In lieu of mirrors, Fresnel lenses can also be used to concentrate heat flux. Either method can be used to quickly vaporize water into steam using sunlight. For example, the sunlight reflected from mirrors heats the PS10 Solar Power Plant, and during the day it can heat water to 285 °C (558.15 K) or 545 °F.
Surface effects
Lighter colors and also whites and metallic substances absorb less illuminating light, and thus heat up less; but otherwise colour makes small difference as regards heat transfer between an object at everyday temperatures and its surroundings, since the dominant emitted wavelengths are nowhere near the visible spectrum, but rather in the far infrared. Emissivities at those wavelengths have little to do with visual emissivities (visible colors); in the far infra-red, most objects have high emissivities. Thus, except in sunlight, the color of clothing makes little difference as regards warmth; likewise, paint color of houses makes little difference to warmth except when the painted part is sunlit.
The main exception to this is shiny metal surfaces, which have low emissivities both in the visible wavelengths and in the far infrared. Such surfaces can be used to reduce heat transfer in both directions; an example of this is the multi-layer insulation used to insulate spacecraft.
Low-emissivity windows in houses are a more complicated technology, since they must have low emissivity at thermal wavelengths while remaining transparent to visible light.
Properties
There are four main properties that characterize thermal radiation:
- Thermal radiation emitted by a body at any temperature consists of a wide range of frequencies. The frequency distribution is given by Planck's law of black-body radiation for an idealized emitter. This is shown in the right-hand diagram.
- The dominant frequency (or color) range of the emitted radiation shifts to higher frequencies as the temperature of the emitter increases. For example, a red hot object radiates mainly in the long wavelengths (red and orange) of the visible band. If it is heated further, it also begins to emit discernible amounts of green and blue light, and the spread of frequencies in the entire visible range cause it to appear white to the human eye; it is white hot. However, even at a white-hot temperature of 2000 K, 99% of the energy of the radiation is still in the infrared. This is determined by Wien's displacement law. In the diagram the peak value for each curve moves to the left as the temperature increases.
- The total amount of radiation of all frequencies increases steeply as the temperature rises; it grows as T4, where T is the absolute temperature of the body. An object at the temperature of a kitchen oven, about twice the room temperature on the absolute temperature scale (600 K vs. 300 K) radiates 16 times as much power per unit area. An object at the temperature of the filament in an incandescent light bulb--roughly 3000 K, or 10 times room temperature—radiates 10,000 times as much energy per unit area. The total radiative intensity of a black body rises as the fourth power of the absolute temperature, as expressed by the Stefan–Boltzmann law. In the plot, the area under each curve grows rapidly as the temperature increases.
- The rate of electromagnetic radiation emitted at a given frequency is proportional to the amount of absorption that it would experience by the source. Thus, a surface that absorbs more red light thermally radiates more red light. This principle applies to all properties of the wave, including wavelength (color), direction, polarization, and even coherence, so that it is quite possible to have thermal radiation which is polarized, coherent, and directional, though polarized and coherent forms are fairly rare in nature.
These properties apply if the distances considered are much larger than the wavelengths contributing to the spectrum (most significant from 8-25 micrometres at 300 K). Indeed, thermal radiation here takes only traveling waves into account. A more sophisticated framework involving electromagnetic theory has to be used for lower distances (near-field thermal radiation).
| °C | Subjective color [2] |
|---|---|
| 480 | faint red glow |
| 580 | dark red |
| 730 | bright red, slightly orange |
| 930 | bright orange |
| 1100 | pale yellowish orange |
| 1300 | yellowish white |
| > 1400 | white (yellowish if seen from a distance through atmosphere) |
Interchange of energy
Thermal radiation is one of the principle mechanisms of heat transfer. It entails the emission of a spectrum of electromagnetic radiation due to an object's temperature. Other mechanisms are convection and conduction. The interplay of energy exchange by thermal radiation is characterized by the following equation:
Here, 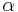 represents the spectral absorption component,
represents the spectral absorption component, 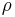 spectral reflection component and
spectral reflection component and 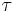 the spectral transmission component. These elements are a function of the wavelength (
the spectral transmission component. These elements are a function of the wavelength (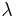 ) of the electromagnetic radiation. The spectral absorption is equal to the emissivity
) of the electromagnetic radiation. The spectral absorption is equal to the emissivity 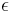 ; this relation is known as Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation. An object is called a black body if, for all frequencies, the following formula applies:
; this relation is known as Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation. An object is called a black body if, for all frequencies, the following formula applies:
In a practical situation and room-temperature setting, humans lose considerable energy due to thermal radiation. However, the energy lost by emitting infrared light is partially regained by absorbing the heat flow due to conduction from surrounding objects, and the remainder resulting from generated heat through metabolism. Human skin has an emissivity of very close to 1.0 .[4] Using the formulas below shows a human, having roughly 2 square meter in surface area, and a temperature of about 307 K, continuously radiates approximately 1000 watts. However, if people are indoors, surrounded by surfaces at 296 K, they receive back about 900 watts from the wall, ceiling, and other surroundings, so the net loss is only about 100 watts. These heat transfer estimates are highly dependent on extrinsic variables, such as wearing clothes, i.e. decreasing total thermal circuit conductivity, therefore reducing total output heat flux. Only truly gray systems (relative equivalent emissivity/absorptivity and no directional transmissivity dependence in all control volume bodies considered) can achieve reasonable steady-state heat flux estimates through the Stefan-Boltzmann law. Encountering this "ideally calculable" situation is virtually impossible (although common engineering procedures surrender the dependency of these unknown variables and "assume" this to be the case). Optimistically, these "gray" approximations will get you close to real solutions, as most divergence from Stefan-Boltzmann solutions is very small (especially in most STP lab controlled environments).
If objects appear white (reflective in the visual spectrum), they are not necessarily equally reflective (and thus non-emissive) in the thermal infrared; e.g., most household radiators are painted white despite the fact that they have to be good thermal radiators. Acrylic and urethane based white paints have 93% blackbody radiation efficiency at room temperature[5] (meaning the term "black body" does not always correspond to the visually perceived color of an object). These materials that do not follow the "black color = high emissivity/absorptivity" caveat will most likely have functional spectral emissivity/absorptivity dependence.
Calculation of radiative heat transfer between groups of object, including a 'cavity' or 'surroundings' requires solution of a set of simultaneous equations using the Radiosity method. In these calculations, the geometrical configuration of the problem is distilled to a set of numbers called view factors, which give the proportion of radiation leaving any given surface that hits another specific surface. These calculations are important in the fields of solar thermal energy, boiler and furnace design and raytraced computer graphics.
A selective surface can be used when energy is being extracted from the sun. For instance, when a green house is made, most of the roof and walls are made out of glass. Glass is transparent in the visible (approximately 0.4 µm<λ<0.8 µm) and near-infrared wavelengths, but opaque to mid- to far-wavelength infrared (approximately λ>3 µm).[6][7] Therefore glass lets in radiation in the visible range, allowing us to be able to see through it, but doesn’t let out radiation that is emitted from objects at or close to room temperature. This traps what we feel as heat. This is known as the greenhouse effect and can be observed by getting into a car that has been sitting in the sun. Selective surfaces can also be used on solar collectors. We can find out how much help a selective surface coating is by looking at the equilibrium temperature of a plate that is being heated through solar radiation. If the plate is receiving a solar irradiation of 1350 W/m2 (minimum is 1325 W/m2on July 4 and maximum is 1418 W/m2on January 3) from the sun the temperature of the plate where the radiation leaving is equal to the radiation being received by the plate is 393 K (248 °F). If the plate has a selective surface with an emissivity of 0.9 and a cut off wavelength of 2.0 µm, the equilibrium temperature is approximately 1250 K (1790 °F). Note that the calculations were made neglecting convective heat transfer and neglecting the solar irradiation absorbed in the clouds/atmosphere for simplicity, however, the theory is still the same for an actual problem. If we have a surface, such as a glass window, with which we would like to reduce the heat transfer from, a clear reflective film with a low emissivity coating can be placed on the interior of the wall. “Low-emittance (low-E) coatings are microscopically thin, virtually invisible, metal or metallic oxide layers deposited on a window or skylight glazing surface primarily to reduce the U-factor by suppressing radiative heat flow”.[8] By adding this coating we are limiting the amount of radiation that leaves the window thus increasing the amount of heat that is retained inside the window.
Radiative heat transfer
The radiative heat transfer from one surface to another is equal to the radiation entering the first surface from the other, minus the radiation leaving the first surface.
- For a black body
Using the reciprocity rule, 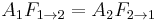 , this simplifies to:
, this simplifies to:
where 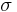 is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
- For a grey body with only two surfaces the heat transfer is equal to:
However, this value can easily change for different circumstances and different equations should be used on a case per case basis.
Radiative power
Thermal radiation power of a black body per unit of solid angle and per unit frequency 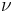 is given by Planck's law as:
is given by Planck's law as:
or
where 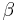 is a constant.
is a constant.
This formula mathematically follows from calculation of spectral distribution of energy in quantized electromagnetic field which is in complete thermal equilibrium with the radiating object. The equation is derived as an infinite sum over all possible frequencies. The energy, 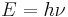 , of each photon is multiplied by the number of states available at that frequency, and the probability that each of those states will be occupied.
, of each photon is multiplied by the number of states available at that frequency, and the probability that each of those states will be occupied.
Integrating the above equation over 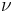 the power output given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law is obtained, as:
the power output given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law is obtained, as:
where the constant of proportionality 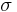 is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant and
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant and  is the radiating surface area.
is the radiating surface area.
Further, the wavelength 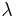 , for which the emission intensity is highest, is given by Wien's Law as:
, for which the emission intensity is highest, is given by Wien's Law as:
For surfaces which are not black bodies, one has to consider the (generally frequency dependent) emissivity factor 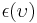 . This factor has to be multiplied with the radiation spectrum formula before integration. If it is taken as a constant, the resulting formula for the power output can be written in a way that contains
. This factor has to be multiplied with the radiation spectrum formula before integration. If it is taken as a constant, the resulting formula for the power output can be written in a way that contains 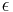 as a factor:
as a factor:
This type of theoretical model, with frequency-independent emissivity lower than that of a perfect black body, is often known as a gray body. For frequency-dependent emissivity, the solution for the integrated power depends on the functional form of the dependence, though in general there is no simple expression for it. Practically speaking, if the emissivity of the body is roughly constant around the peak emission wavelength, the gray body model tends to work fairly well since the weight of the curve around the peak emission tends to dominate the integral.
Constants
Definitions of constants used in the above equations:
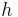 |
Planck's constant | 6.626 0693(11)×10−34 J·s = 4.135 667 43(35)×10−15 eV·s |
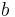 |
Wien's displacement constant | 2.897 7685(51)×10−3 m·K |
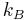 |
Boltzmann constant | 1.380 6505(24)×10−23 J·K−1 = 8.617 343(15)×10−5 eV·K−1 |
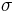 |
Stefan–Boltzmann constant | 5.670 400(40)×10−8 W·m−2·K−4 |
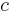 |
Speed of light | 299,792,458 m·s−1 |
Variables
Definitions of variables, with example values:
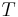 |
Absolute temperature | For units used above, must be in kelvin (e.g. Average surface temperature on Earth = 288 K) |
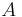 |
Surface area | Acuboid = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac; Acylinder = 2π·r(h + r); Asphere = 4π·r2 |
See also
- Incandescence
- Infrared photography
- Interior radiation control coating
- Planck radiation
- Sakuma–Hattori equation
- Thermal dose unit
- Thermography
References
- ^ K. Huang, Statistical Mechanics (2003), p.278
- ^ K. Huang, Statistical Mechanics (2003), p280
- ^ a b S. Blundell, K. Blundell (2006). Concepts in Modern Physics. Oxford University Press. p. 247. ISBN 978-0-19-856769-1.
- ^ R. Bowling Barnes (24 May 1963). "Thermography of the Human Body Infrared-radiant energy provides new concepts and instrumentation for medical diagnosis". Science 140 (3569): 870–877. Bibcode 1963Sci...140..870B. doi:10.1126/science.140.3569.870.
- ^ S. Tanemura, M. Tazawa, P. Jing, T. Miki, K. Yoshimura, K. Igarashi, M. Ohishi, K. Shimono, M. Adachi, Optical Properties and Radiative Cooling Power of White Paints,[1] ISES 1999 Solar World Congress
- ^ a b c Heat and Mass Transfer, Yunus A. Cengel and Afshin J. Ghajar, 4th Edition
- ^ Infrared#Different_regions_in_the_infrared Short-wavelength infrared is 1.4-3µm, Mid-wavelength infrared is 3-8µm
- ^ http://www.efficientwindows.org/lowe.cfm
Related reading:
- Siegel, John R. Howell, Robert; Howell. John R. (2001-11). Thermal radiation heat transfer. New York: Taylor & Francis, Inc.. pp. (xix - xxvi list of symbols for thermal radiation formulas). ISBN 9781560328391. http://books.google.com/?id=O389yQ0-fecC&pg=PA1&dq=Thermal+radiation. Retrieved 2009-07-23.
External links
- Black Body Emission Calculator
- Heat Transfer
- Thermal Radiation
- Atmospheric Radiation
- Infrared Temperature Calibration 101
|
||||||||||||||||||||||